In this topic, we will learn about Transmission Media in computer networks and their types like Wired media and Wireless media
What is Transmission Media?
Transmission Media are the communication channels through which data is transmitted. When two or more devices want to communicate or want to share data then they need the communication channel known as transmission media.
Transmission media are the carriers for transmitting the data from receiver to sender. There is a physical path established between the sender and receiver, in other words, it provides the path to travel the data information in it.
A transmission medium is a path through which the data will transfer from one place to another in the form of binary digits because they are encoded into a signal and transmitted over the medium which is called a transmission medium.
All the broadcasts on your TV, Internet, and YouTube are transferred through the transmission medium which uses copper cable wires, fiber networks, and many more mediums, through which we are able to watch all these broadcasts at our homes.
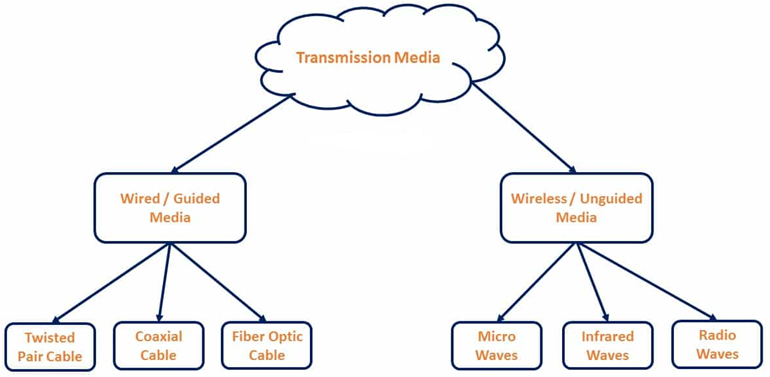
Types of Transmission Media.
Wired, Bound, or Guided Transmission Medium.
- Twisted Pair Cables
- Coaxial Cables
- Fiber Optic Cables
Wireless, Unbound, or Unguided Transmission Medium.
- Microwaves
- Infrared Waves
- Radio Waves
Wired Transmission Media
Guided transmission media have a physical existence, which means we can touch them.
Wired transmission, as the name specifies their work, is in cable forms or wire forms, used to send and receive data from one place to another by using Cables like Twisted Pair Cables, Coaxial Cables, Or Fiber Optic Cables.
It is also known as Guided transmission media because the path is guided and passes through the cables in particular directions only.
It is also known as Bounded transmission media because the data signals are bounded, and just travel according to the cabling system.
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted Pair Cabling is the widest-used network in transmission mediums. As before the period of wireless, all the transmission of data was transferred through cables or wired only.
It’s a pair of copper wires, with two conductors(basically copper), and are twisted together to form a single wire with an insulation plastic rapped on it.
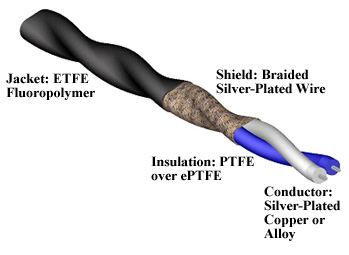
The use of two wires is for the purpose of data transmission, one is for the real signal and the other for the ground reference, which are coated with color to identify them separately.
These wires are used to reduce noise and any type of disturbance especially crosstalk and are generally used as telephone lines for voice and data transmission
There are two types of twisted-pair cables
- Unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP)
- Shielded Twisted pair(STP)
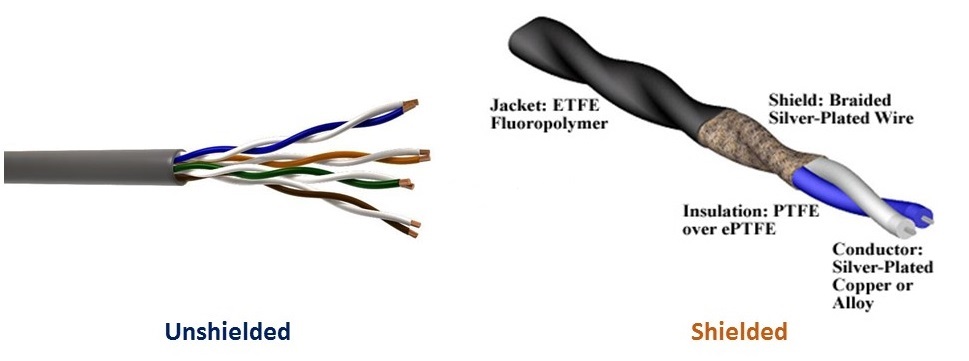
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- Unshielded is just a simple cable wire with insulation plastic rapped on it.
- There is no shield or copper foil rapped on it.
- They are low-cost, cabling wires usually used for LANs network and for telephone connections
- They are not used for high bandwidth, because the material used in it is not sufficient for transferring high bandwidth.
Shielded Twisted Pair(STP)
- These cables used metal foil rapped on them as an extra layer after the plastic wrapper.
- Shielded cables are used to prevent electromagnetic noise and also remove the crosstalk problems.
- Generally, used for high-bandwidth transfer.
- These are costlier than Unshielded and coaxial cables.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables- two copper wires
The inner/core is a copper wire made of a solid conductor used for data transmission, which is enclosed with a solid insulating sheath of plastic
Then the outer layer is of copper wires wrapped on the insulating sheath which protects it from external electromagnetic attenuation(noise)

This is again covered with a plastic cover which protects the inner layers from physical damage of fire and water.
Coaxial cables are distinguished by their Radio Government (RG) rating. Which shows the usage in their particular area.
Standards of coaxial cables:
50-Ohm RG-7 or RG-11: Used in Ethernet or “thicknet”
50-Ohm RG-58: Used in thin Ethernet, or “cheapnet”
75-Ohm RG-59: Used in Cable Television at Home
93-Ohm RG-62: Used in ARCNET.
Fiber Optic Cables:
Fiber optic cables are the highest standard cables made up of thin glass plastic which is used to transfer the data signals in the form of digital light over thousands of miles.
There is no interference that disturbs fiber optic cables.
As their high data transmission property, they are designed for transferring long-distance.
Fiber optic uses lightly pulsed which is generated by small lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
The inner core of fiber optic cables is made of a thin glass which is as thin as the size of your hair, through which the light pulses or signals are transmitted.
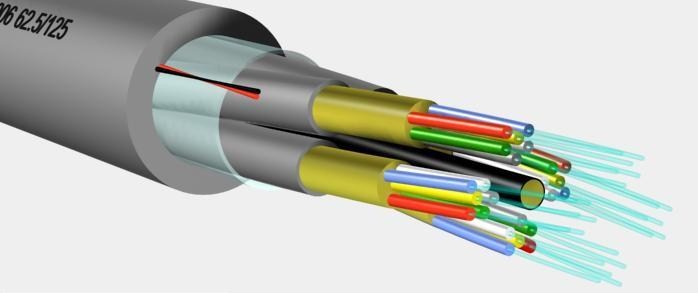
Then the inner core is surrounded by a layer of cladding which is used to reflect the light back into the core. Cladding prevents the light signals from remaining inside the glass core and avoids the loss of signals.
Then comes the outer layer wrapped in cladding which is a synthetic yellow or white type of hair used to protect the sheath of a glass of fiber core.
And at the outermost layer which is the cable’s jacket or sheathing, which is the outer body of the cable, protects from fire, water, and natural damage.
- Fiber optics is mostly used on the Internet because of the higher bandwidth.
- Fiber optic cables are used in Medical fields because of their flexibility and thinness for insertion into the lungs, and body vessels, and are also used in surgery.
- Because of their higher bandwidth, they are used on the Server sides
- They are used in Hydrophones, SONAR, and seismic uses in submarines, also used in aircraft.
- Fiber optic cables are highly used in scientific machines and used as invention areas by various government organizations like DRDO, ISRO, etc.
Wireless Medium, Unguided or unbound transmission medium
Wireless is defined by the name itself as wireless means without wires, which does not have a physical existence between two devices, because it is wirelessly.
In wireless devices, Data transmits electromagnetically in waves in the presence of air without any physical contact. Wireless devices use Antennas on both sides on the receiving and sending side.
Antennas of Wireless devices are attached to the electric circuit of a computer device and convert the digital data into electromagnetic waves and transfer them over a required frequency range.
There is a receptor at the receiving side that receives the signals and converts them back into digital data.
The main feature of wireless media is they can travel a large distance using the earth’s atmosphere.
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
According to the Economic Times
“Electromagnetic waves are emitted through electric appliances when come in contact with a magnetic field. An electromagnetic field is produced when a charged particle is accelerated. EM waves are the combination of the electric and magnetic fields that travel in free space using the speed of light c.
In vacuums, these waves travel at a speed of 3 X 10 8 m.s -1
Electromagnetic waves can travel in Air, in a solid material, in a vacuum, they can travel anywhere, whereas other waves(like sound waves, water waves) require a medium to travel”
Radio Waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation that have wavelengths in their electromagnetic spectrum. Radio wave frequencies are from 300 gigahertz (GHz) to 30 hertz.
Radio waves are artificial waves transmitted by transmitters and received by radio receivers, by using antennas. Radio waves are used in communication for mobile, radio communication, broadcasting, radar and radio navigation systems, communications satellites, wireless computer networks, etc.
The main feature of Radiowaves is that they can receive signals from an antenna that is traveling in their path.
Microwaves
Microwaves are also a type of electromagnetic radiation waves that are used for communication, radar, and cooking purposes.
Microwaves have frequency ranges from 1 gigahertz (GHz) to 300 GHz and have a wavelength from 30 cm to 1 millimeter.
Microwaves are used in various satellite communications, navigation systems, radar systems, remote sensors, and short-range communications also, because they travel in a straight line, whereas others travel in all directions.
Infrared waves.
Infrared waves were discovered in 1800, by William Herschel.
Infrared waves are also a part of wireless transmission, which are always around our atmosphere and we are surrounded by it like our eyes cannot see infrared but, our body feels its heat.
These waves are very high-frequency range which is used in our TV remote controls, automatic sensors, and wireless devices like printers, mice, keyboards, etc.
As these are very high frequency they cannot travel through a solid region like the Wall of a room, you have noticed that your home remote cannot change TV channels from other rooms.
Summary:
- Transmission media are of two types Guided and Unguided media.
- Twisted pair cables have more than one pair of cables twisted together to reduce the electromagnetic interference, one is for current and the other for removing attenuation.
- Telephone Lines used Twisted pair cables. There are two types of twisted pair cables, Shielded and Unshielded twisted pair cable.
- Fiber optic cables are the best transmission media for higher bandwidth, because of long-distance used purpose.
You can also read these topics:
What are Transmission Mediums?
Components of Computer Network
What is Network Topology? and its types
Different Types of LAN, MAN, PAN, WAN
What is a Computer Network and why do we need it?
What is Data Transmission Modes? Types of Transmission Modes
What is Switching in Computer Networks? and types of Switching