In this tutorial, we will discuss what is switching?, types of switching techniques like Packet Switching, Message Switching, and Circuit Switching, and also the difference between them
What is Switching?
Switching is a technique in a computer network that decides the best route for transmission of data, whenever there are multiple paths in a large network.
In Big networks, there are multiple route links and if the sender wants to send the information to the receiver then the information has to pass through multiple routes and switches help to route the information through the best path that is reliable and fast deliverable.
Also Read: Data Transmission Modes
In simple terms, when data or information is to be passed from one computer to another computer then that information does not reach directly to the destination, it passes through many nodes that are in the route path, and information switches through these nodes.
Types of Switching Techniques.
- Circuit Switching
- Message Switching
- Packet Switching

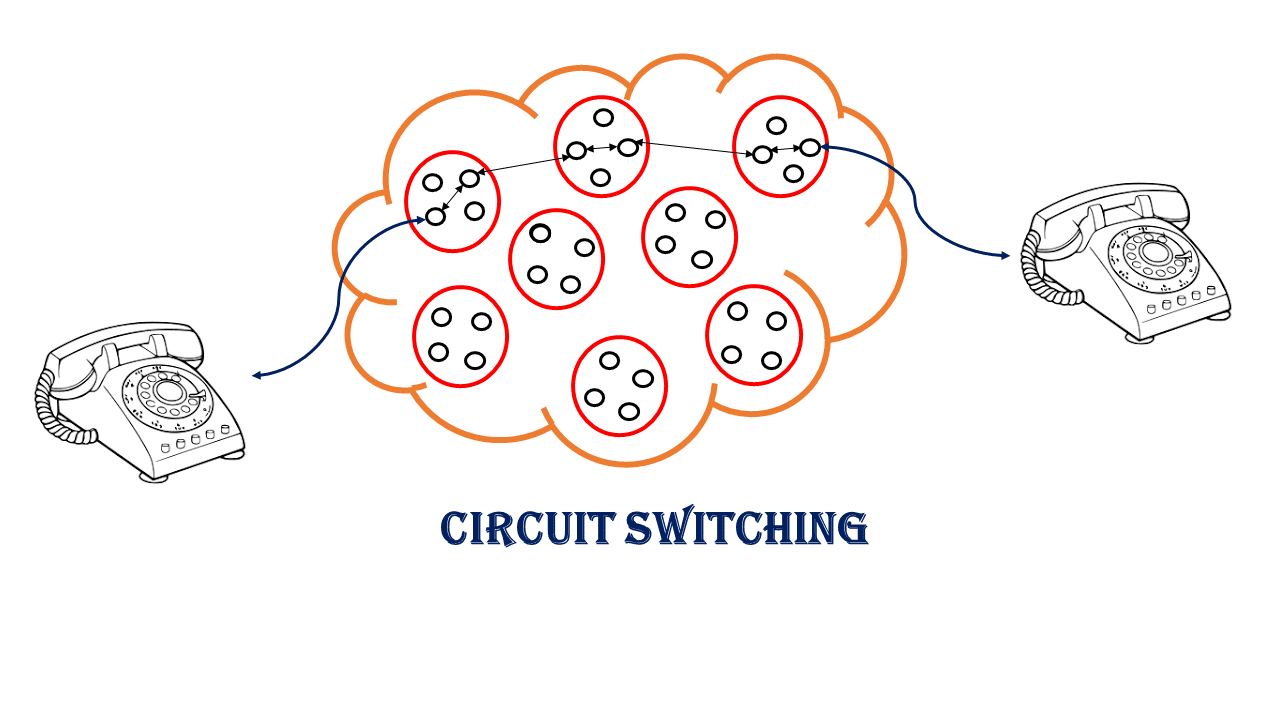
Circuit Switching
Circuit Switching is a technique of sharing and communicating between sender and receiver it establishes a dedicated path between sender and receiver.
The sender and receiver during the communication use the path through which they communicate their information and circuit switching gives them a path to communicate and no other device interrupts their path because it is a dedicated path only for them.
Switching techniques provide the sender and receiver with a pre-specific route that is reserved for only sender and receiver and this path is connected with them until the communication is over. Both the devices are connected with this specific Circuit route and only use this path for their communication, no other device can communicate through this specific route.
The Circuit Switching technique was designed and used in the early analog telephone network where we use circuit switching to connect physical devices in the telephone network.
Circuit switching is used when the user wants to send voice, data, or video, then the request signals are sent to the receiver and then the receiver sends it back for the acknowledgment to ensure the availability of the dedicated path, and after receiving the acknowledgment, dedicate path transfers the information.

In-circuit Switching communication has three phases
Establishment of Circuit: when we call to any of our friend and relative
Transfer of Data: when he receives the call and shares the information.
Circuit Disconnect: Communication ends and one of you ends the call and the circuit disconnects.
Circuit Switching is of two types
- Space Division Switching
- Time Division Switching
Space Division Switching: The paths in this circuit are separated from each other. It is designed for analog networks and can be used for both analog and digital switching.
Space Division Switches are of two types:
- Crossbar Switch: In the Crossbar switch there are n input lines and n output lines. The Crossbar switch has n2 intersection points which are called crosspoints.
- Multistage Switch: This switching is made by splitting the crossbar switch into many smaller units and then interconnecting them, which reduces the number of crosspoints, and there one path fails, then a new path is available.
Time Division Switching: This switching comes under digital switching techniques, in which the Pulse Code Modulated signals are present at the input and the output ports. When the sender and receiver receive and re-transmit the message in a different time slot, is called Time Division Switching.
Advantages of Circuit Switching
- It has a dedicated link for both receiver and sender which provides them a guaranteed data transmission.
- Transfer data without any delay because the path is dedicated and only used by the sender and receiver, so there is no waiting time and no disturbance.
- Continuous transfer of data is best for long-distance transmission.
The disadvantage of Circuit Switching
- Other devices cannot communicate through it because once the path is dedicated to only the sender and receiver, no other device can communicate through it.
- The connection uses more bandwidth because of continuous data transmission, it is more expensive.
- Takes a long time to establish a connection approx 9-10 seconds, during which you cannot transmit any data.
Message switching
Message Switching techniques is just a stored-forward-stored, as it doesn’t establish a dedicated path between sender and receiver, and if the sender wants to send the message to the destination point then the message has to pass through all path because there is no dedicated path between sender and receiver.
In Message switching, when one node sends a message to another node then there are many nodes between the sender node and the receiver node, and the message is passed to each and every node which is in the path, and each node stores the message and then forward the message to another node, which is much time-consuming.
The message-switching technique acts as an independent entity for each message.

Advantages of Message Switching
- The message is passed through all the communication devices, so there is the best use of bandwidth in a single message-transferring
- Traffic is reduced because the message is stored in temporary nodes, and the priority of the message can be used to manage the network.
The disadvantage of Message Switching
- Delay in message due to storing and forwarding facility in every node.
- The message is stored in each node and if space is not enough in the forwarding node then the previous node has to wait until there is enough space, and then the previous node again has to send the message to the next node.
Packet Switching
Packet Switching is the technique of sending a message in which the whole message is divided into smaller pieces of information which is known as a packet, and these packets are traveled through the network and decide their shortest path to reach the destination node.
For this, every packet has a unique sequence number which makes it easy for the receiving node to identify them at the receiving end.

The packet of each piece contains the information of their source address, a destination address, sequence number, etc through which the destination node easily identifies them, they are routed all over the internetwork independently and reach the desired node only.
There are two types of Packet Switching
Datagram Packet switching: This is the packet-switching technique where packets are called Datagrams also known as connectionless switching and considered as independent entities. This packet contains information about the destination and then the switch uses this information and forwards the packets to the destination.
Virtual Circuit Switching: Virtual Circuit Switching is called connection-oriented switching because in this switching a preplanned route is established before the messages are sent where the path is fixed during the duration of the connection.
Virtual Circuit Switching is of two types
Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVCs): It is used when the connection is for a long duration (days or weeks) and can be changed only by the network manager.
Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC): It creates dynamically on a per-call basis and disconnected when the call ends

What is a Trunk Call?
In 1902, When the telephone was introduced, if someone has to call then the same telephone exchange has to call, but if he wants to call in another city, then he has to book a “Trunk Call“, then the telephone exchange of that particular city has to call and ask them to connect the telephone exchange of that particular exchange, and this takes about 1 to 3 hours.
you can read the following topics:
What are Transmission Mediums?
Components of Computer Network
What is Network Topology? and its types
Different Types of LAN, MAN, PAN, WAN
What is a Computer Network and why do we need it?
What is Data Transmission Modes? Types of Transmission Modes
What is Switching in Computer Networks? and types of Switching